This chapter explores one of the most important non-linear data structures, i.e., trees. Various kinds of trees are available with different features. You will start learning with the most important tree structure, i.e., the binary tree which is a finite set of elements that is either empty or further divided into sub-trees.
There are two ways to represent binary trees. These are:
- Using arrays
- Using Linked lists
The Non-Linear Data structure
The data structures that you have learned so far were merely linear - strings, arrays, lists, stacks, and queues. One of the most important nonlinear data structure is the tree. Trees are mainly used to represent data containing the hierarchical relationship between elements, example: records, family trees, and table of contents. A tree may be defined as a finite set 'T' of one or more nodes such that there is a node designated as the root of the tree and the other nodes are divided into n>=0 disjoint sets T1, T2, T3, T4 …. Tn are called the subtrees or children of the root.
What is a Binary Tree?
A binary tree is a special type of tree in which every node or vertex has either no child node or one child node or two child nodes. A binary tree is an important class of a tree data structure in which a node can have at most two children.
Child node in a binary tree on the left is termed as 'left child node' and node in the right is termed as the 'right child node.'
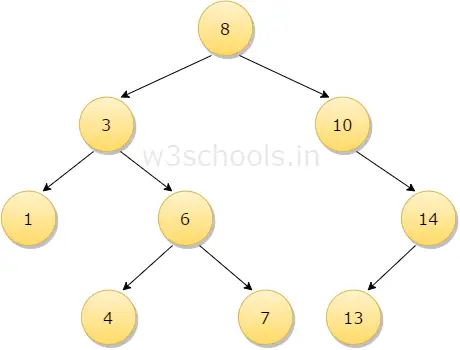
In the figure mentioned below, the root node 8 has two children 3 and 10; then this two child node again acts as a parent node for 1 and 6 for left parent node 3 and 14 for right parent node 10. Similarly, 6 and 14 has a child node.
A binary tree may also be defined as follows:
- A binary tree is either an empty tree
- Or a binary tree consists of a node called the root node, a left subtree and a right subtree, both of which will act as a binary tree once again
Applications of Binary Tree
Binary trees are used to represent a nonlinear data structure. There are various forms of Binary trees. Binary trees play a vital role in a software application. One of the most important applications of the Binary tree is in the searching algorithm.
A general tree is defined as a nonempty finite set T of elements called nodes such that:
- The tree contains the root element
- The remaining elements of the tree form an ordered collection of zeros and more disjoint trees T1, T2, T3, T4 …. Tn which are called subtrees.
Types of Binary Trees are
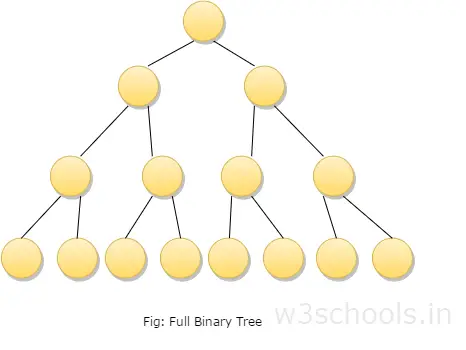
- A full binary tree which is also called as proper binary tree or 2-tree is a tree in which all the node other than the leaves has exact two children.
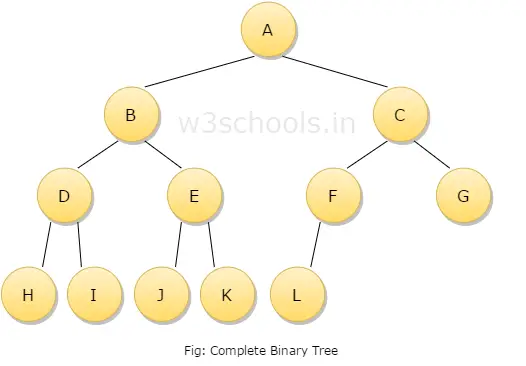
- A complete binary tree is a binary tree in which at every level, except possibly the last, has to be filled and all nodes are as far left as possible.
- A binary tree can be converted into an extended binary tree by adding new nodes to its leaf nodes and to the nodes that have only one child. These new nodes are added in such a way that all the nodes in the resultant tree have either zero or two children. It is also called 2 - tree.
- The threaded Binary tree is the tree which is represented using pointers the empty subtrees are set to NULL, i.e. 'left' pointer of the node whose left child is empty subtree is normally set to NULL. These large numbers of pointer sets are used in different ways.