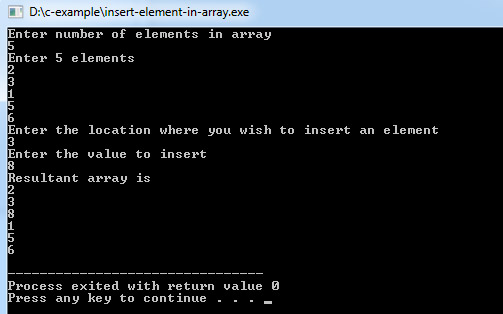
This C program code will insert an element into an array, and it does not mean increasing size of the array.
For example consider an array n[10] having four elements:
n[0] = 1, n[1] = 2, n[2] = 3 and n[3] = 4
And suppose you want to insert a new value 60 at first position of array. i.e. n[0] = 60, so we have to move elements one step below so after insertion
n[1] = 1 which was n[0] initially, n[2] = 2, n[3] = 3 and n[4] = 4.
Program:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int array[50], position, c, n, value;
printf("Enter number of elements in the array\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("Enter %d elements\n", n);
for (c = 0; c < n; c++)
scanf("%d", &array[c]);
printf("Please enter the location where you want to insert an new element\n");
scanf("%d", &position);
printf("Please enter the value\n");
scanf("%d", &value);
for (c = n - 1; c >= position - 1; c--)
array[c+1] = array[c];
array[position-1] = value;
printf("Resultant array is\n");
for (c = 0; c <= n; c++)
printf("%d\n", array[c]);
return 0;
}Program Output: