This tutorial has a detailed description of PHP Syntax. It's essential for you before proceeding to learn more advanced PHP features.
PHP Tags
PHP is designed to work with HTML, so you can easily write and embed PHP code with HTML. A PHP code block begins with <?php tag and ends with ?> tag.
Syntax:
<?php
//your php code goes here
?>PHP with HTML
echo is a command in PHP for writing output data to the browser, and at the end of each PHP statement, we are required to write a (semicolon) as you see in the below example code. Otherwise, PHP will report a syntax error if you write another statement.
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Hello World Program in PHP</title>
</head>
<body>
<?php echo "Hello World"; ?>
</body>
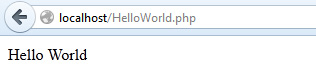
</html>To run this PHP program, write the above code in any text editor and save it to your web server under the www directory with a .php extension.
Once it's done, start the server, go to localhost, and type in the path of your file, i.e., http://localhost/HelloWorld.php
Program Output:
How to write and execute PHP
Comments in PHP
The PHP interpreter ignores the comment block; it can be used anywhere in the program to add info about the program or code block, which can be helpful for the programmer to understand the code easily in the feature.
In PHP, we can use // or # to make a single-line comment and /* and */ to make a large comment block.
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>PHP Comments Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<?php
// This is single line commented text, and
# This is another single line commented text
/*
This is
a Multi-lines comment
block area
*/
?>
</body>
</html>