An array is one of the data structures in C++ that can store a fixed-size sequential collection of elements of the same data type. This tutorial will teach you how to use array in C++
Define an Array in C++
Syntax:
type arrayName [ arraySize ];An array type can be any valid C++ data type, and array size must be an integer constant greater than zero.
Example:
double salary[15000];Initialize an Array in C++
An array can be initialized at the time of declaration, as demonstrated in the example below.
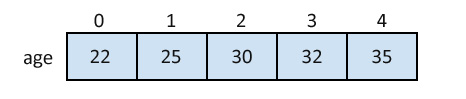
int age[5] = {22,25,30,32,35};The example below shows how each element is initialized separately in the loop.
int newArray[5];
int n = 0;
// Initializing elements of the array separately
for(n=0; n<sizeof(newArray)/sizeof(newArray[0]); n++)
{
newArray[n] = n;
}A Pictorial Representation of the Array
Accessing Array Elements in C++
int newArray[10];
int n = 0;
// Initializing elements of the array separately
for(n=0; n<sizeof(newArray)/sizeof(newArray[0]); n++)
{
newArray[n] = n;
}
int a = newArray[5]; // Assigning 5th element of array value to integer 'a'.Example:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <iomanip>
using std::setw;
int main () {
int newArray[5];
int n = 0, p =0;
// Initializing elements of array seperately
for (n=0; n<sizeof(newArray)/sizeof(newArray[0]); n++) {
newArray[n] = n+50;
}
// print heading
cout << "Element" << setw(10) << "Value" << endl;
// print element's value in loop
for (p=0; p<sizeof(newArray)/sizeof(newArray[0]); p++) {
cout << setw(5) << p << setw(10) << newArray[p] << endl;
}
return 0;
}Program Output:
Element Value
0 50
1 51
2 52
3 53
4 54