C++ if Statements control the flow of the program based on conditions. If the expression evaluates to true, it executes certain statements within the if block; Otherwise, execution will get skipped. It is the simplest way to modify the control flow in a C++ program. This tutorial will teach you how to use if Statements in C++.
Programmers can use "if Statements" in C++ in various forms depending on the situation and code complexity.
- if Statement
- if-else Statement
- Nested if-else Statement
- else-if Ladder
The basic format of the if Statement is:
Syntax:
if(test_expression)
{
Statement 1;
Statement 2;
...
}'Statement n' can be a statement or a set of statements, and if the test expression evaluates to true, the statement block will get executed or skipped.
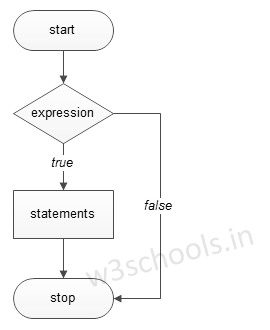
Figure - Flowchart of if Statement:
Example of a C++ Program to Demonstrate if Statement:
Example:
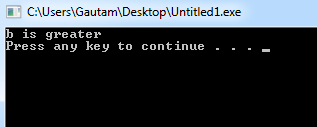
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 15, b = 20;
if (b > a) {
cout << "b is greater" << endl;
}
system("PAUSE");
}Program Output:
Example:
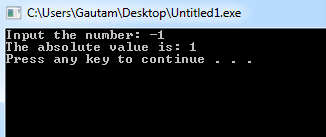
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int number;
cout << "Input the number: "; cin >> number;
/* check whether the number is negative number */
if(number < 0)
{
/* If it is a negative then convert it into positive. */
number = -number;
cout<<"The absolute value is: "<< number<<endl;
system("PAUSE");
}
} Program Output: