The cloud infrastructure is closely related to its architecture and comprises many cloud components that are loosely connected.
The broad divisions of cloud architecture are:
- Front-end
- Back-end
It is the back-end responsibility to provide data security for cloud users and the traffic control mechanism. The server also provides the middleware, which helps to connect devices and communicate with each other.
Figure - Cloud Computing Architecture:
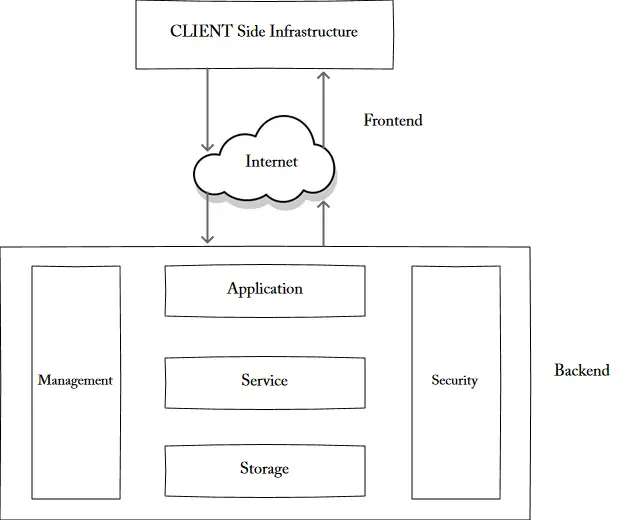
Businesses used cloud infrastructures to work with these applications. Unlike subscription-based pricing models, the cloud's payment structure enables the user to subscribe to vendor services, and cloud infrastructures are paid on a 'pay-per-use' basis.
The cloud technology architecture also consists of front-end platforms (as read in the early chapters) called the cloud client, which comprises servers, thin & fat clients, tablets & mobile devices. The interaction is done through middleware or via web-browser or virtual sessions. According to Jason Bloomberg of ZapThink, the cloud-oriented architecture can essentially be the building block of IoT (Internet of Things) in which anything can be connected to the internet. Cloud architecture is a combination of both services-oriented architecture & event-driven architecture. SO cloud architecture encompasses all elements of the cloud environment.