The array is a data structure in C programming that can store a fixed-size sequential collection of elements of the same data type. In this tutorial, you will learn to use arrays in C programming.
For example, if you want to store ten numbers, it is easier to define an array of 10 lengths instead of ten variables.
In the C programming language, an array can be One-Dimensional, Two-Dimensional, and Multidimensional.
Define an Array in C
Syntax:
type arrayName [ size ];This is called a one-dimensional array. An array type can be any valid C data type, and the array size must be an integer constant greater than zero.
Example:
double amount[5];Initialize an Array in C
Arrays can be initialized at declaration time:
Example:
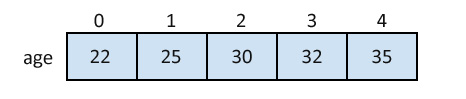
int age[5] = {22,25,30,32,35};Initializing each element separately in a loop:
int myArray[5];
int n = 0;
// Initializing elements of the array separately.
for(n=0;n<sizeof(myArray)/sizeof(myArray[0]);n++)
{
myArray[n] = n;
}A Pictorial Representation of the Array:
Accessing Array Elements in C
Example:
int myArray[5];
int n = 0;
// Initializing elements of array seperately.
for(n=0;n<sizeof(myArray)/sizeof(myArray[0]);n++)
{
myArray[n] = n;
}
int a = myArray[3]; // Assigning 3rd element of array value to integer 'a'.C Arrays - Video Tutorial
Please watch this video tutorial to understand "C Arrays" in depth.