A data-type in C programming is a set of values and is determined to act on those values. C provides various types of data-types, allowing the programmer to select the appropriate type for the variable to set its value.
The data-type in a programming language is the collection of data with values having fixed meanings and characteristics. Some of them are an integer, floating point, character, etc. Usually, programming languages specify the range values for a given data-type.
C Data Types are used to:
- Identify the type of a variable when it is declared.
- Identify the type of return value of a function.
- Identify the type of parameter expected by a function.
- Primary(Built-in) Data Types:
void,int,char,double, andfloat. - Derived Data Types: Array, References, and Pointers.
- User Defined Data Types: Structure, Union, and Enumeration.
Primary Data Types
Every C compiler supports five primary data types:
void
| As the name suggests, it holds no value and is generally used for specifying the type of function or what it returns. If the function has a void type, it means that the function will not return any value. |
int
| Used to denote an integer type. |
char
| Used to denote a character type. |
float, double
| Used to denote a floating point type. |
int *, float *, char *
| Used to denote a pointer type. |
Three more data types have been added in C99:
_Bool_Complex_Imaginary
Declaration of Primary Data Types with Variable Names
After taking suitable variable names, they need to be assigned with a data type. This is how the data types are used along with variables:
Example:
int age;
char letter;
float height, width;
Derived Data Types
C supports three derived data types:
| Data Types | Description |
|---|---|
| Arrays | Arrays are sequences of data items having homogeneous values. They have adjacent memory locations to store values. |
| References | Function pointers allow referencing functions with a particular signature. |
| Pointers | These powerful C features are used to access the memory and deal with their addresses. |
User Defined Data Types
C allows the type definition feature, which allows programmers to define their identifier representing an existing data type. There are three such types:
| Data Types | Description |
|---|---|
| Structure | It is a package of variables of different types under the same name. This is done to handle the data efficiently. Here the "struct" keyword is used to define a structure.
|
| Union | These allow storing various data types in the same memory location. Programmers can define a union with different members, but only a single member can contain a value at a given time. |
| Enum | Enumeration is a special data type that consists of integral constants. Each of them is assigned a specific name. "enum" keyword is used to define the enumerated data type.
|
Data Types and Variable Declarations in C
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 4000; // positive integer data type
float b = 5.2324; // float data type
char c = 'Z'; // char data type
long d = 41657; // long positive integer data type
long e = -21556; // long -ve integer data type
int f = -185; // -ve integer data type
short g = 130; // short +ve integer data type
short h = -130; // short -ve integer data type
double i = 4.1234567890; // double float data type
float j = -3.55; // float data type
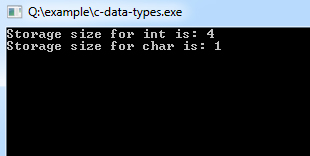
}The storage representation and machine instructions differ from machine to machine. sizeof operator can use to get the exact size of a type or a variable on a particular platform.
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <limits.h>
int main()
{
printf("Storage size for int is: %d \n", sizeof(int));
printf("Storage size for char is: %d \n", sizeof(char));
return 0;
}Program Output: