C Constants are like a variable, except their value never changes during execution once defined. This tutorial describes C Constants.
C Constant is the most fundamental and essential part of the C programming language. Constants in C are the fixed values used in a program, and their value remains the same during the entire program execution.
- Constants are also called literals.
- Constants can be any of the data types.
- It is considered best practice to define constants using only upper-case names.
Constant Definition in C
Syntax:
const type constant_name;const keyword defines a constant in C.
Example:
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
const int SIDE = 10;
int area;
area = SIDE*SIDE;
printf("The area of the square with side: %d is: %d sq. units", SIDE, area);
}Program Output:
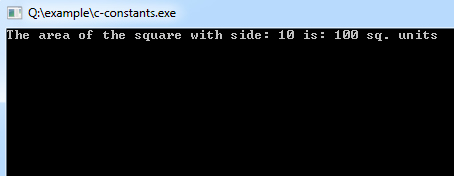
Putting const either before or after the type is possible.
int const SIDE = 10;or
const int SIDE = 10;Constant Types in C
Constants are categorized into two basic types, each of which has subtypes/categories. These are:
- Numeric Constants
- Integer Constants
- Real Constants
- Character Constants
- Single Character Constants
- String Constants
- Backslash Character Constants
Integer Constant
It refers to a sequence of digits. Integers are of three types viz:
- Decimal Integer
- Octal Integer
- Hexadecimal Integer
Example:
15, -265, 0, 99818, +25, 045, 0X6Real constant
The numbers containing fractional parts like 99.25 are called real or floating points constant.
Single Character Constants
It simply contains a single character enclosed within ' and ' (a pair of the single quote). It is to be noted that the character '8' is not the same as 8. Character constants have specific integer values known as ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange).
Example:
'X', '5', ';'String Constants
These are a sequence of characters enclosed in double quotes, and they may include letters, digits, special characters, and blank spaces. Note that "G" and 'G' are different - because "G" represents a string as it is enclosed within a pair of double quotes, whereas 'G' means a single character.
Example:
"Hello!", "2015", "2+1"Backslash character constants
C supports some character constants having a backslash in front of it. The lists of backslash characters have a specific meaning known to the compiler. They are also termed "Escape Sequences".
Example:
\t is used to give a tab \n is used to give a new line
| Constants | Meaning |
|---|---|
\a
| beep sound |
\b
| backspace |
\f
| form feed |
\n
| new line |
\r
| carriage return |
\t
| horizontal tab |
\v
| vertical tab |
\'
| single quote |
\"
| double quote |
\\
| backslash |
\0
| null |