An array is a one of the data structure in Java, that can store a fixed-size sequential collection of elements of the same data type.
For many large applications, there may arise some situations that need a single name to store multiple values. To process such significant amount of data, programmers need strong data types that would facilitate the efficient contiguous bulk amount of storage facility, accessing and dealing with such data items. So, arrays are used in Java. In this tutorial, you will learn about what arrays are and what the types are and how they are used within a Java program.
Define an Array in Java
The syntax of declaring array variables is:
Syntax:
datatype[] identifier; //preferred way
or
datatype identifier[];The syntax used for instantiating arrays within a Java program is:
Example:
char[] refVar;
int[] refVar;
short[] refVar;
long[] refVar;
int[][] refVar; //two-dimensional arrayInitialize an Array in Java
By using new operator array can be initialized.
Example:
int[] age = new int[5]; //5 is the size of array.Arrays can be initialized at declaration time also.
Example:
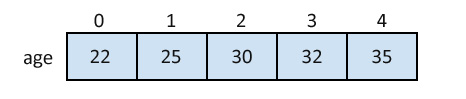
int age[5]={22,25,30,32,35};Initializing each element separately in the loop.
Example:
public class Sample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] newArray = new int[5];
// Initializing elements of array seperately
for (int n = 0; n < newArray.length; n++) {
newArray[n] = n;
}
}
}A Pictorial Representation of Array
Accessing Array Elements in Java
Example:
public class Sample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] newArray = new int[5];
// Initializing elements of array seperately
for (int n = 0; n < newArray.length; n++) {
newArray[n] = n;
}
System.out.println(newArray[2]); // Assigning 2nd element of array value
}
}
Program Output: