Sometimes it is necessary for the program to execute the statement several times, and Java loops execute a block of commands a specified number of times until a condition is met. In this chapter, you will learn about all the looping statements of Java along with their use.
What is Loop?
A computer is the most suitable machine to perform repetitive tasks and can tirelessly do a task tens of thousands of times. Every programming language has the feature to instruct to do such repetitive tasks with the help of certain form of statements. The process of repeatedly executing a collection of statement is called looping. The statements get executed many numbers of times based on the condition. But if the condition is given in such logic that the repetition continues any number of times with no fixed condition to stop looping those statements, then this type of looping is called infinite looping.
Java supports many looping features which enable programmers to develop concise Java programs with repetitive processes.
All are slightly different and provides loops for different situations.
Figure - Flowchart of Looping:
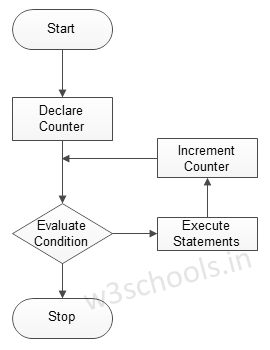
Java Loop Control Statements
Loop control statements are used to change the normal sequence of execution of the loop.
| Statement | Syntax | Description |
|---|---|---|
| break statement | break; | Is used to terminate loop or switch statements. |
| continue statement | continue; | Is used to suspend the execution of current loop iteration and transfer control to the loop for the next iteration. |
| goto statement | goto labelName;labelName: statement; | It transfers current program execution sequence to some other part of the program. |